2009 is the dawn of virtual currency. An anonymous person created Bitcoin and paved the way for a decentralized financial system. However, the concept of smart contracts existed back in time.
If the anonymous and tamper-proof finance of blockchain impresses you, it is imperative to know that smart contracts are behind this functionality of blockchain. Thus, there is a direct link between smart contracts and blockchain.
But what is a smart contract? A computer program or lines of code for automatic actions in a deal between two parties is a smart contract. Be mindful that a smart contract is neither smart nor a contract. It is merely a replacement of a third party in a deal between people who don’t trust each other.
That’s it for a smart contract? Well, it’s just the tip of the iceberg. Delve into reading this comprehensive guide to understand essential concepts of:
- Smart contract,
- Working and features of smart contracts,
- Real-world applications of smart contracts,
- Its pros and cons, and much more.
We are confident that you will have adequate knowledge to understand why smart contracts are important in today’s world after a thorough read of this guide.
Smart Contract in Blockchain – An Overview
Before we talk about smart contracts, think of a vending machine at a convenience store or on a roadside. The machine stores plenty of things you may need. However, you can’t get a single thing unless you insert the right amount of cash into it. What makes the vending machine so smart to calculate everything with accuracy and expertise?
It is the program or lines of code within the machine. When you insert enough cash for a specific product and press the button, the vending machine’s program offers you that product. It acts like a mediator between you and the machine. This is what we call smart contracts in technical terms.
In other words, a smart contract is a self-executing and automated software that performs the transaction or deal once the defined objectives are completed. It is just like the program inside the vending machine.
You must know that smart contracts are not documents of any sort, including corporate or legal. They are just lines of code with defined actions to cut off the need for a third-party mediator. This speeds up transactions and blockchain operations.
A Brief History of Smart Contracts
The year is 1994 and a computer scientist in the United States of America proposes a unique and advanced system of computers for financial matters. We are talking about the American computer scientist, Nick Szabo. The person who is perceived to be the anonymous Bitcoin creator Satoshi Nakamoto.
Though he denied this claim himself, the mystery of the first cryptocurrency persists. The reason behind calling Szabo the creator of Bitcoin is the idea of the first virtual currency which he called Bit Gold.
In 1994, Nick Szabo published a paper defining smart contracts and their usability. According to him, a smart contract is a computerized protocol for the execution of transactions in regard to the terms of a contract. He also proposed the combination of securities and derivatives, such as bonds, options, and futures.
The purpose of this idea was cost-effective transactions, standardized contracts, faster transactions and borderless trades. On top of that, this was the practical implementation of computer concepts into financial advancement.
Blockchain and Smart Contracts – The Connection
Blockchain is the modern internet, storage, and financial system. It is among the leading innovations of this century due to its splendid functions. Provided that, blockchain is the go-to option for everyone, including individuals, businesses, and institutions.
According to a report on Statista, the adoption rate of blockchain technology is skyrocketing at 10% annually. The banking sector is the highest shareholder in the global adoption of this innovative technology. And why not? You get security, scalability and interoperability in a single place.
However, the success of blockchain would not have been possible if smart contracts didn’t exist. Smart contracts add to automation, efficiency, transparency, trust, and many more of the blockchain technology.
How Does Smart Contract Work?
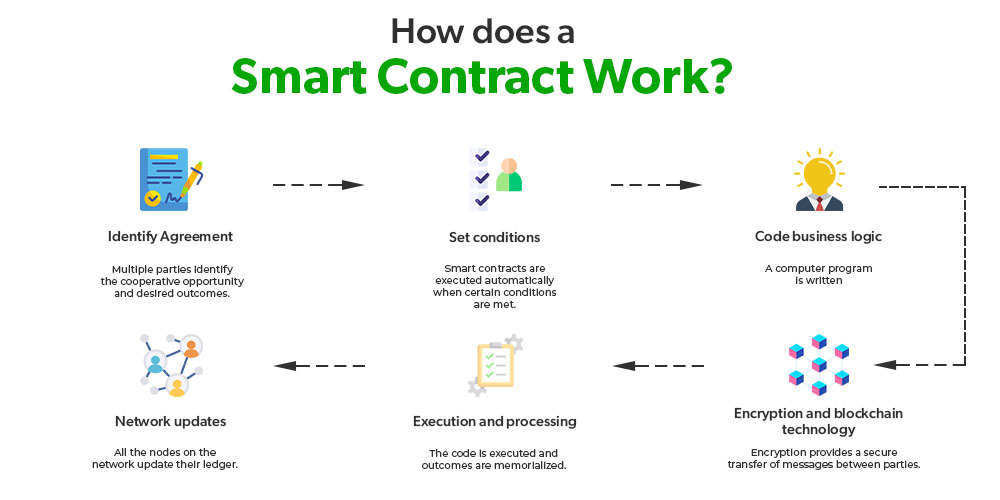
Since smart contracts are computer programs for automated transactions and contracts, a programming language is a must. There are multiple programming languages and technologies for the development of smart contracts. The most popular and most used one is Ethereum’s Solidity.
A smart contract works on a blockchain and the logic behind its functionality is an if/else condition. For instance, the developer will design the smart contract with this condition:
- If X happens, execute Y action.
When it comes to developing a smart contract, any programmer with a firm grip on Solidity or other programming languages can create one. Sometimes, a group of independent or freelance developers also create a smart contract and deploy it on the blockchain.
It is a smart contract that defines various events and actions associated with it. For instance, it defines:
- Interactions of users with smart contracts
- Who can interact with it,
- Time of the interaction
- The input and output of the interaction with smart contracts, etc.
Real-Time Analogy of Smart Contract Working
Smart contracts offer a variety of applications. We will look up the use of smart contracts in a global trade here. Suppose a person from the US wants to trade with another person in the UK. Since both lack mutual understanding, fair trade will require a third party to look after the business transactions.
In this case, the smart contract will act as the middleman for automated business transactions. It will define and execute the terms of the contract automatically, such as:
- If the products from the UK reach the US on the agreed time, execute X amount to the supplier
- If it reaches late for 1 day, execute payment X per cent less than the agreed term
- If it doesn’t arrive by X date, execute no payment.
In this case, the control is in the hands of an unbiased, reliable and inhumane smart contract. Thus, there exists no concern about trust and fraud. This is just one example while smart contracts have applications in multiple industries. We’ll cover them in detail moving forward.
What are the Major Types of Smart Contracts?
Smart contracts provide blockchain and organizations with the real power of decentralization. It cuts off requirements for banks, lawyers, authorities, etc. We can understand this concept much better by looking at different types of smart contracts.
They are as follows:
1. Smart Legal Contract
Law and order are key to a fair trade and business transaction. Without compliance with legal protocols, you can’t expect a just transaction. Therefore, every contract acts as a binding document from the legal doctrine of a country. If a party fails, intentionally or accidentally, to breach the terms of the contract, they will be liable before the court of law.
However, the surety of a legal and enforcement action against a lawbreaker may not be certain due to several reasons. On the contrary, smart contracts act on top of the immutable and transparent blockchain.
Smart legal contracts define legal terms for both parties in a clear and articulate manner. Thus, breaching it becomes a difficult task, offering higher transparency and trust in a business transaction.
2. Decentralized Autonomous Organizations (DAO)
A decentralized autonomous organization or DAO is the best example of a democratic and hierarchy-resistant system of business and organization. In this model of enterprise, a smart contract contains terms and conditions instead of a president or CEO.
The blockchain is the core foundation of the enterprise with stakeholders acting as working members of the organization. Within a smart contract remain the rules and regulations of the company operations. This also governs funds allocation with equity-based division of finances.
VitaDAO is a prime example of a DAO that has a robust smart contract on the backend. This is an automated organization that empowers scientific research without the governance of a single person or group of people.
3. Application Logic Contracts
Have you ever imagined a contract between two different machines? Application Logic Contracts (ALCs) are those smart contracts which create the mutual connectivity between software, hardware, and operating systems.
The best examples of ALCs are the Internet of Things (IoT) and interoperable blockchains, such as Chainlink, Ethereum, etc. These smart contracts regulate communication to the extent of fair usage and authentic information handling.
Key Features of Smart Contracts
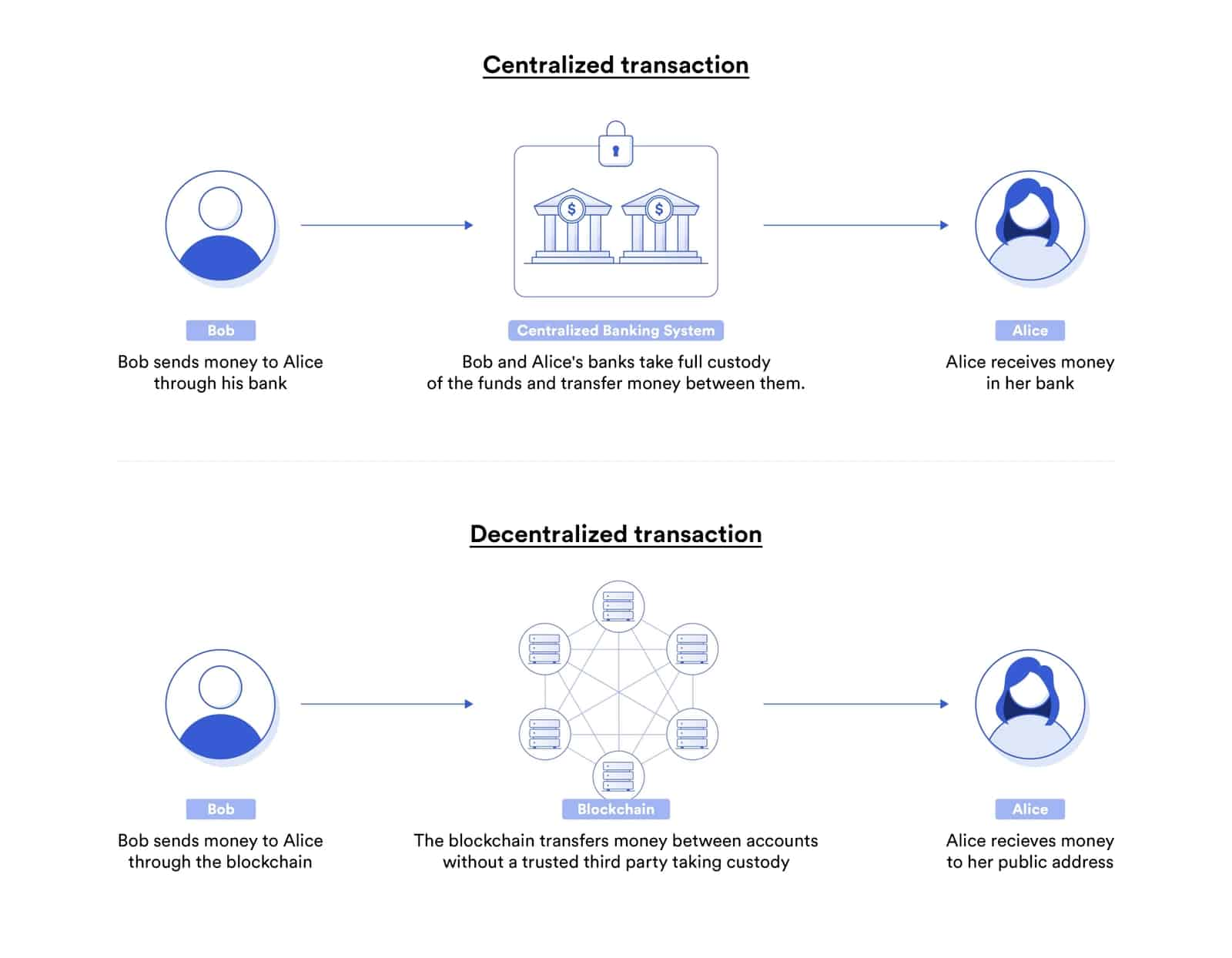
Upholding commitment in a business deal or transaction is the most important factor. In traditional digital agreements, this exposes parties to various risks. However, smart contracts have come a long way in solving this issue.
Why do we need smart contracts? In the above image, you can see the difference between centralized and decentralized digital payments. Due to the risk of contract breaches, organizations and businesses depend on banks and centralized authorities, which cost them deep pockets.
On the contrary, smart contracts remove the need for centralized authorities as well as the risks associated with digital payments.
These features will help you understand the vitality of smart contracts.
1. Speed and Efficiency
Smart contracts speed up the transaction time and facilitate faster business deals. It may sound confusing but it is what it is. The reason behind the efficiency and faster speed of smart contract-based transactions is the automation of multiple tasks. That includes:
- Escrow
- Maintenance
- Execution
- Settlement
- Legal actions (If any of the parties breaches the terms of the contract)
Automating these essentials of a financial deal makes the process incredibly fast. In traditional deals and business affairs, manual data and its authentication consume time. A smart contract takes another path and offers the same functionality even better and faster.
2. Accuracy
Smart contracts are computerized programs programmed by expert developers. Due to several tests and compilation, the chance for a mistake in the execution of an event seems non-existing with smart contracts.
Therefore, smart contracts are highly accurate with no human error. This way, business transactions performed via smart contracts are just, fair, and unbiased.
Be mindful that the action of a smart contract is in the hands of its developer. If the person writes a faulty code, the smart contract will generate false actions, leading to a miserable organizational contract and deals. Thus, monitoring and testing the code of a smart contract is important to avoid risks of failure.
3. Trust and Transparency
Smart contracts work on a single source of truth principle. This means that every party has access to similar data as the other all the time. It is due to the transparency of blockchain technology, making smart contracts transparent as well.
Chain of record is another characteristic of blockchain, which is also found in smart contracts. This means that every change to the data adds on to make another block on an existing blockchain. Thus, any individual in the deal can access records of the transaction at any moment.
4. Security
The excellent thing about blockchain technology is decentralization. It means that there exists no single point of failure. This is because blockchain functions on a governance model involving multiple validators and the real-time owner of the assets.
On the other hand, the traditional financial system relies on a centralized bank. The banks have complete control and authority over the assets of a business or an individual. Any problem with the bank means disruption and inconvenience to the entire community of users.
Since smart contracts run on top of blockchains, it is highly secure due to the immutable nature of the decentralized blockchain.
Use Cases of Smart Contracts
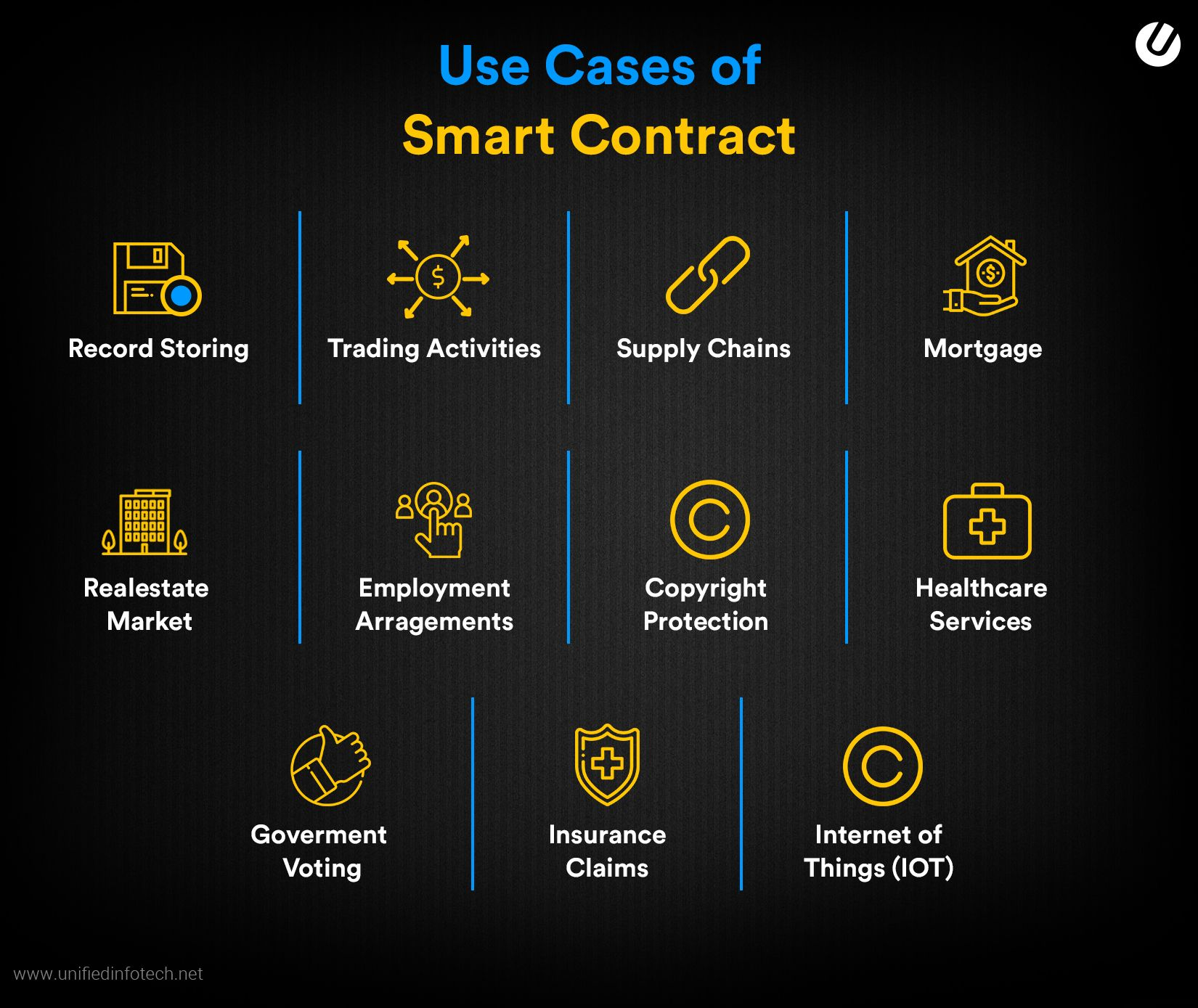
Smart contracts have transformed the financial as well as digital ecosystem in a few years. From decentralized finance to gaming, insurance, and more, you will observe multiple use cases of smart contracts.
Here are some of the top industrial applications of smart contracts:
Decentralized Finance (DeFi) Applications
If you have to define DeFi in a simple term, it’ll go like this: A system that recreates traditional financial instruments in a decentralized ecosystem. For instance, the currency that uses smart contracts and blockchain technology is cryptocurrency and it is a DeFi application.
There are multiple examples of DeFi applications. They include:
- Trading options,
- Stablecoins, exchanges,
- Non-fungible tokens
- Web3, etc.
Smart contracts play a vital role in the development and maintenance of DeFi applications. This is due to its versatile usability and functionality.
Efficacy of Medications
Healthcare is an evergreen industry that needs severe care for the well-being of all humankind. Over the past few years, the healthcare sector has partnered with multiple technological innovations, such as artificial intelligence (AI), smart contracts, blockchain, and more.
According to Harvard University, biotechnology and digital health technology have established a milestone in healthcare. It is essential to note that medicines are key to the growth and effectiveness of medical care.
Smart contracts ensure the efficacy of medicines by transparency in medicines’ supply management. For example, IBM’s Pharma Portal is one of the blockchain-based applications that monitors and tracks the supply chain of pharmaceuticals for reliable data.
Trust in Retailer-Supplier Relationships
Visibility and transparency in smart contracts are top features that help in solving disputes and trust issues. Chances are that vendors and suppliers may get into a dispute over a contract. However, smart contracts ensure trust and accuracy throughout the transaction.
As we mentioned in the real-world example of international trade, smart contracts keep funds in escrow and release them once the shipment of the product is done on time. This saves parties in a business deal from unwanted problems.
Borderless Trade
Smart contracts also reduce friction and pave the way for international and borderless trade. You can create a smart contract that determines the rules and terms for international trade. This automates and smoothens the transaction and shipment.
However, an international trading company, We.Trade is an IBM Blockchain-based organization that offers effortless and effective services to global traders. By reducing risks and friction between parties, you can rely on the smart contract that we.trade will develop for your deal.
Electrical Polls and Elections
In the democratic ecosystem, voter manipulation has become a major concern. A fair and accurate election is no longer possible due to various loopholes in the currency electoral system of many countries.
Smart contracts offer a reliable solution to this problem. Smart contracts introduce cryptographic encryption that stores electoral data in a well-protected ledger. This makes it harder for anyone to manipulate the results.
Real Estate
Just like a business deal, property transfer in real estate is a big problem that involves risks of fraud. With smart contracts in place, realtors and property owners can safeguard their lands and properties’ data using the blockchain’s decentralized ledger.
This is also beneficial for the buyer of the property. The autonomous and trustworthy execution of smart contracts eases the process of real estate up to a significant extent.
Gaming and Non-Fungible Tokens (NFTs)
Are you a fan of video gaming? Video games have evolved a lot over time. The immersiveness and in-game actions have reached infinity. Thus, the global video gaming market has reached heights of success. It is a billion-dollar industry with a global market size of $282.30 billion.
The same goes for non-fungible tokens. NFTs refer to any unique digital thing on the internet, be it art, in-game assets, painting, etc. NFTs and video games are two modern areas that can offer financial benefits to a greater extent.
The best thing about them is the use of tamper-proof execution of actions or asset management due to smart contracts. Thus, smart contracts are the foundational architecture behind the working of decentralized games and NFTs.
Challenges with Smart Contracts
Regardless of how beneficial smart contracts are, they also face some challenges. In the future, we must tackle these challenges to gain a more reliable and lucrative experience with smart contracts and blockchain.
Some of the challenges that smart contracts have are as follows:
1. Permanent and Rigid
As we already covered in our guide, smart contracts are tamper-proof. This implies that nobody, even the developer of the smart contract can change the rules and terms of the contract once it is developed. And even if they do, it costs time and money. This rigidity can become a problem for the global utility of smart contracts as the legal circumstances of countries vary.
2. Contradicting GDPR
GDPR stands for the General Data Protection Regulation. This is a legal document that grants the right to be forgotten by its citizens. In other words, if a user wants to remove and/or delete their digital data, they are legally allowed to do so.
However, smart contracts with their decentralized and blockchain technology never allow the deletion and removal of data. Once the data goes up on the ledger, it will remain there until the blockchain exists.
3. Loopholes and Security Shortcomings
Smart contracts have a drawback when it comes to recording unquantifiable data. Some industries, such as finance, agriculture, and others, have quantifiable data. Smart contracts for these areas offer no problem. However, creating a fully functional smart contract for businesses with creative and legal work will expose developers to loads of problems.
Moreover, several security and cyber attacks have occurred on various blockchains that use smart contracts. In spite of the top-notch and matchless security infrastructure, malicious actors and social engineers overcoming them are a major loophole.
Conclusion
Smart contracts are the backbone of blockchain technology and modern technological innovations like cryptocurrency, IoT, etc. They are software with a program to automatically perform an action when the coded conditions are met.
A smart contract offers multiple benefits, including:
- Faster transaction,
- Trustworthy and transparent business transactions,
- Effective and secure international trade,
- Immutable and tamper-proof chain of record for organizational data, etc.
Be mindful that not all smart contracts need blockchain to function as independent smart contracts can also exist. And smart contracts are not smart – they do what they are programmed to do, nothing more and nothing less.
FAQs
What is a smart contract in simple terms?
A smart contract is a computerized mediator between two parties in a business deal or trade that performs actions according to its programmed system, which includes certain conditions and actions against them.
What are examples of smart contracts?
Some of the top examples of smart contracts are Ethereum, Binance Smart Chain, Avalanche, etc. They automate the crypto and blockchain functions of the respective network.
Can a smart contract fail?
A smart contract is software just like the one you use to read this article or play a game. Failure of a smart contract is only possible due to faulty code or program. Since it is tested before release, the chances of a smart contract failing are minimal.
What is the future of smart contracts?
Based on the ongoing research and development, it seems that the future of smart contracts will be prosperous for the transformation of transactions and trades. With legal frameworks in the smart contract, we will witness the full potential of smart contracts in the future.
Is smart contract an AI?
Smart contracts are not artificial intelligence but AI-powered smart contracts exist. Since AI holds the power to write code and develop various applications, AI-based smart contracts are no exception.






